
Thin Film Transistor (TFT) is an electronic circuit to control the brightness of pixels in a display. It is composed of several layers – Source/Drain, Gate, Active Layer - and is divided by the characters of TFT materials. Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon (LTPS) is one of the types of TFT Active Layer that enables current flow for electron transportation. LTPS is an upgraded material of amorphous silicon (a-Si) to increase electron mobility by changing the character of a-Si.
For Materials of display TFT, a-Si or LTPS is widely used according to its purpose. When amorphous silicon (a-Si) is heated by a laser, a-Si crystallizes and transforms into polycrystalline silicon, which refers to LTPS. The reason why they are called low-temperature even though it is made by a hot laser is that the temperature of the process underwent in 450 degrees that don’t deform the glass substrate, compared to High-temperature Polycrystalline silicon (HTPS).
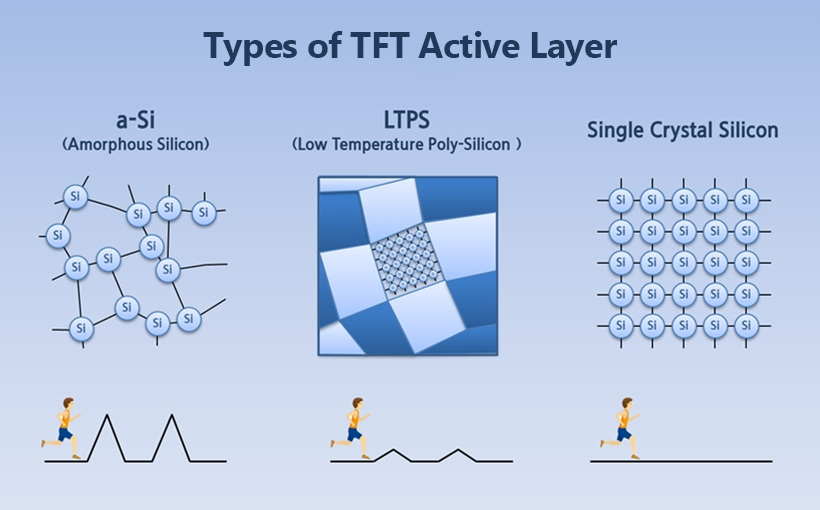
The superiority of TFT depends on whether the current flows well, that is the higher mobility of electrons, the better the performance. Therefore, in order to make it similar to single crystalline silicon, which is the most idealistic form for electron movement, a-Si in disordered form recrystallizes to ordered single-crystalline silicon to increase the performance and efficiency of TFT. When the electrons move on the border of each region, they are slow down, but once they enter the crystalline region, the electron mobility becomes as fast as single-crystal silicon.
If the electrons move quickly, they can not only perform the operation of the TFT circuit rapidly but also send the desired amount of current in a short time so that it is advantageous for a high-resolution display panel that requires a dense circuit configuration. Therefore, LTPS is currently used as the representative TFT for displays for high-resolution smartphones.




