
A polymer with a high level of thermal stability, polyimide also boasts high levels of mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation. Thanks to these traits, polyimide is used not only in displays, but also in various IT sectors including electric and electronics - ranging from solar cells to memory chips.
On top of being lighter than other materials, polyimide is also flexible and bendable — which enables manufacturing lighter and smaller products.
When manufacturing displays, polyimide has a wide spectrum of applications, including substrates and cover windows.

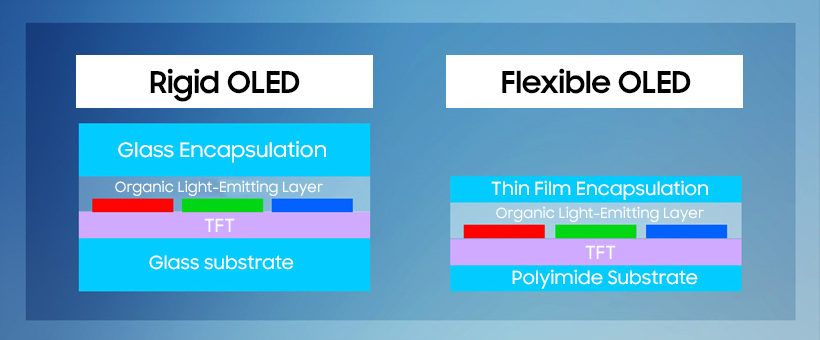
While regular displays are produced using glass substrates, flexible OLED displays require polyimide instead of rigid glass.
The process of manufacturing flexible OLED displays is as follows: First, polyimide is applied on the surface of the glass substrate, often referred to as carrier glass. This is followed by the TFT, evaporation, and encapsulation process, after which the carrier glass is detached by a laser.
Thermal resistance is crucial for display substrates as they must be able to withstand high heat during the manufacturing process. Polyimide withstands temperatures ranging from -273°C to 400°C, enough to say it has an excellent thermal resistance.
Because it is made of a plastic material that is light and flexible, polyimide is ideal as the substrate for manufacturing flexible OLED displays.
Polyimide can be bent or folded without getting broken, which is why it’s also a popular choice for manufacturing cover windows. When used in a cover window, polyimide’s unique yellow tint is removed to ensure the transparency of the cover window.



