Those who familiar with the Japanese animation 'Galaxy Express 999' might remember that the main character Tetsuro wanted a machine body, giving him the ability to live forever. What was once considered only science fiction is becoming a reality right in front of our eyes.
A recent breakthrough in 4D printing technology in bioengineering enables shaping human bone structures. 4D printing can also change nerve tissues, skeletal muscles, and ligaments attached to skeletons - allowing people to ‘print’ shape-shifting 4D life materials. Due to its more advanced nature than conventional 3D printing technology, 4-dimensional printing is expected to revolutionize life sciences, nanoscience, and aerospace industries, taking theoretical ideas from Science Fiction into surreal real-life realizations.
3D Printing? 4D Printing!
3D printing refers to the revolutionary implementation of three-dimensional processing by stacking materials one by one. 3D bio-printed hearts and 3D printing prosthetic limbs have now become possible. Technically, people could stop buying clothes altogether and print clothes every day since 3D printers print on fabric just like ink does on paper.

The next evolution of 3D printing is 4D printing with 'Material' as the key differentiator. Using a 3D printer, 4D printer prints outsmart materials that can be self-modified. While traditional 3D printers produce desired shapes in a three-dimensional space, 4D printers add another dimension; Time. In other words, external stimuli such as temperature, humidity, and vibrations enable 4D printed objects to reshape themselves or self-assemble over time.
Skylar Tibbits, a founder and co-director of the Self-Assembly Lab and associate professor in MIT's Department of Architecture, coined the term 4D printing and introduced it to the public during his ‘The Emergence of 4D Printing’ TED talk speech in 2013. Tibbits’ introduction of 4D printing focuses on self-assembly and self-transformation technology; the ability to change shape and properties over time breathes life into inanimate 4D objects - making 'Galaxy Express 999' machine bodies a real possibility.
Regeneration of Muscle and Bone Tissue
The medical and healthcare industries are actively exploring the realms of 3D printing due to the increasing availability of print customization. Medical 3D printing applications have expanded over the years and now include implants, artificial bones, artificial organs, and medical aids. However, the given technology sees restrictions in regards to materials and printing output. 4D printing has emerged as an improvement, making it an anticipatory alternative among many medical and healthcare experts.
Recently, a Korean research team announced amazing results in regenerating animal muscles and bones using 4D printing technology. Researchers designed a microchannel scaffold made of a collagen and hydroxyapatite combination. Hydroxyapatite, the main mineral of which dental enamel and dentin are composed, is a widely used ingredient for dental implants, artificial bones, and cosmetics. The microchannels have both increased bone tissue formation and induced growth of blood vessels near the graft site in a mouse model. The research team believes that the designed scaffold can have multiple applications with biomimetic structures, such as bones/ligaments, nervous tissue, and skeletal muscle, and is currently conducting research accordingly. This may be the beginning of the many applications of body regeneration but have much potential.
World’s First Pen-based 4D Printing
Imagine creating an object simply by drawing with a pen. Researchers in Korea have developed the world's first 4D printing technology that can directly transform pen-drawn 2D precursors into 3D geometries. “2D-to-3D transformation of pen drawings is facilitated by surface tension–driven capillary peeling and floating of dried ink film when the drawing is dipped into an aqueous monomer solution. Selective control of the floating and anchoring parts of a 2D precursor allowed the 2D drawing to transform into the designed 3D structure (ScienceAdvances).” The core of the technology lies in the principle that dried ink does not dissolve in water and floats.
The pen-based 4D printing process is simple and intuitive. To make the desired product, you first “draw” with two types of board marker ink; One is a floating ink containing surfactant, and the other is an anchoring ink without surfactant, which can be used to draw the floating parts and anchoring parts of a drawing. Once water is poured, ink without surfactants allows the drawing to stay intact. However, ink containing surfactants causes the drawing to float and changes shapes when water is added.
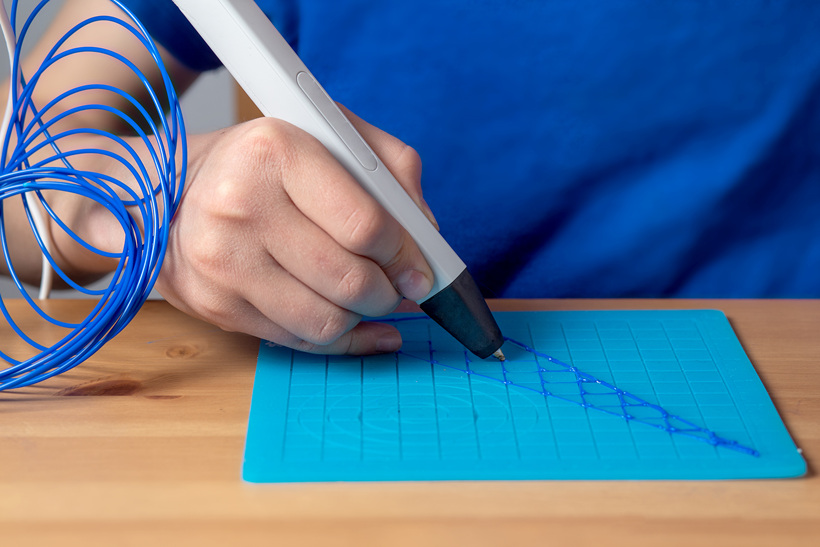

Great discoveries usually spark from small discoveries in our daily lives: It is said that the researchers were originally inspired by observing children play with water and ink and noticing that ink drawings do not mix with water.
So what are the benefits of pen-based 4D printing? It can save time 10-100x times more than that of 3D printing. "If it takes an hour to build one 3D object, 4D printing can produce 120 in the given time," according to the researchers. Once this technology is commercialized, it is expected to drastically reduce the production time of existing 3D printers and easily create three-dimensional objects.
Customizable Clothes with 4D Printing
Is it possible to print clothes with 3D printers? The answer is ‘Yes’, but how would clothes made by 4D printers be different from those made by 3D technology? Founded by graduates of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), 3D printing design studio, Nervous System revealed the Kinematics Dress. Made up of 2,279 unique triangular panel pieces connected with over 3,316 hinges, the Kinematics Dress is the world’s first 4D printed dress.
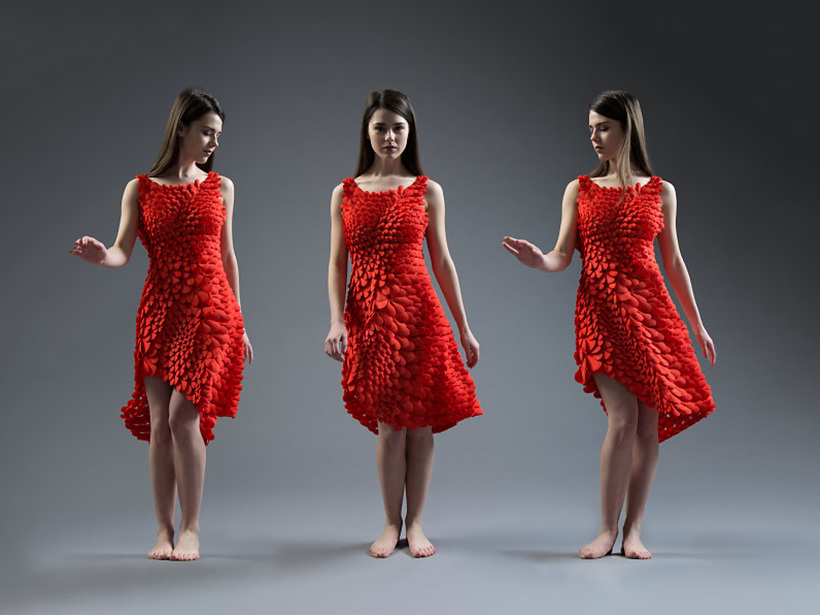

Engineers from Nervous System got the inspiration for the dress from the process of creating bracelets using 3D printers. Their original goal was to create a singular object bigger than a bracelet. “When it’s made, it’s simply pulled out of the print bed, all in one piece and without any assembly required (3D Printing Industry).” Once unfurled, it transforms into a gorgeous dress.
The key difference between this dress and other outfits printed with 3D technology is that it is capable of shape-changing to fit the human body. Since the patterns of the pieces are interconnected, they are modified to fit the body shape of each person. Although its current form is limited to a net-like texture, it will one day be possible to customize outfits that look like ready-made clothes from factories.
Dream Car Becomes Reality with 4D printing
It seems that 4D printing technology will be able to revolutionize the automotive sector. The potential lies in shape memory alloy, which easily restores the original shape by stimulating heat or vibration. 4D printing can also alter the shape of wheels depending on the road's environment. Is it absurd to believe that in the future, car wheels will automatically change based on the steepness of the road? BMW’s ‘Vision Next 100’ concept car brings light to the endless possibilities of 4D printed vehicles.
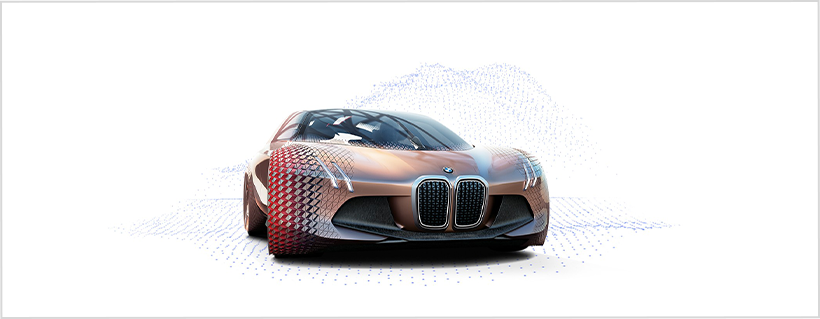
The Vision Next 100 consists of innovative designs and features that can only be seen in movies such as ‘Transformers’. Many are simply struck with disbelief as they struggle to comprehend how an automobile can come across as a transformative robot or even a living creature. In the interior design, the car physically adjusts to enhance the driver’s comfort with autonomous driving sensors kicking in, the steering wheel, and center console retracting - allowing people to easily lie down or rest.
Future Shaped by 4D Printing
The core of 4D printing is self-modification/self-assembling technology. Smart materials, such as shape memory alloys that can be transformed should be used. With more scientific breakthroughs, the diversity of smart materials used for 4D printing will extend of human life as envisioned by many. Cancer-destroying/drug-elivering nanorobots entering human bodies will become a tangible outcome of the promising future technology.

Major end-use applications of 4D printing technology are expected to impact various industries. For architecture and automobile industries, large structures were originally difficult to produce using 3D printers but now possible via 4D printing technology. Military 4D printing market opportunity also exists for military camouflage that changes according to the environment and for temporary building structures in times of war/emergency. Implementations in the aviation and space industries will play a big role too. Despite being a novel technology, the future of 4D printing holds great potential and vast opportunities.


