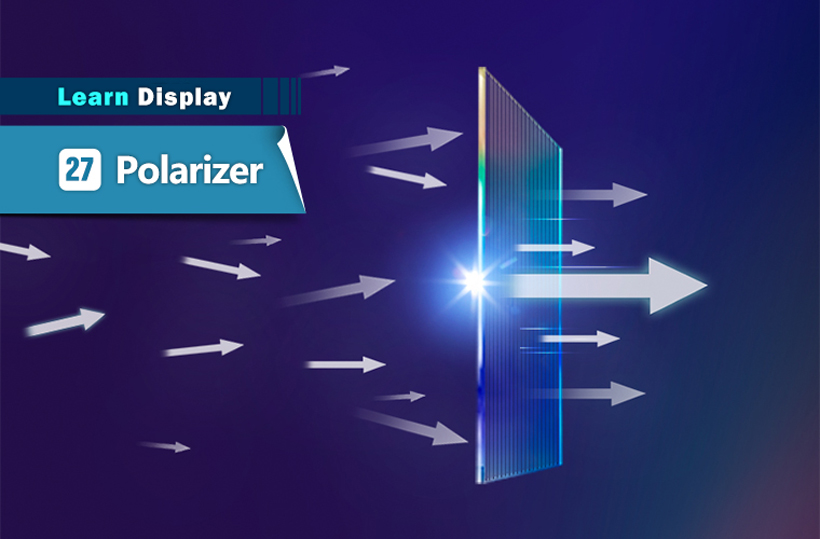
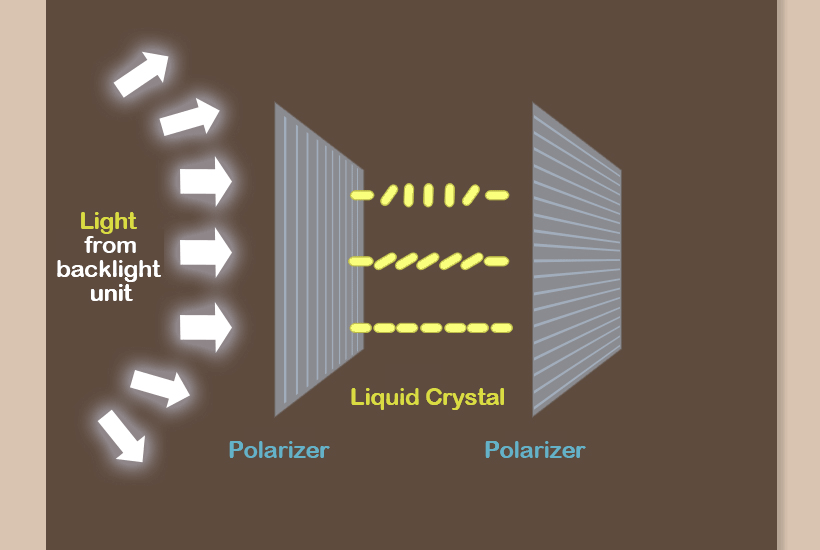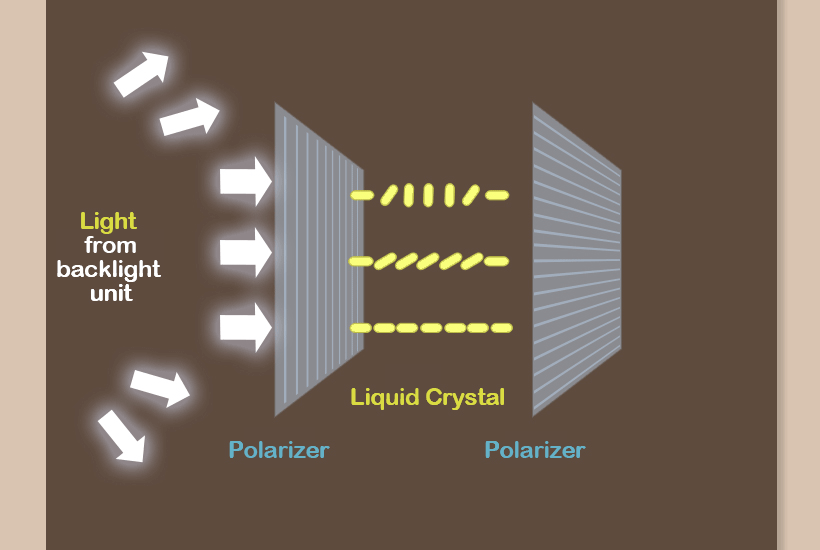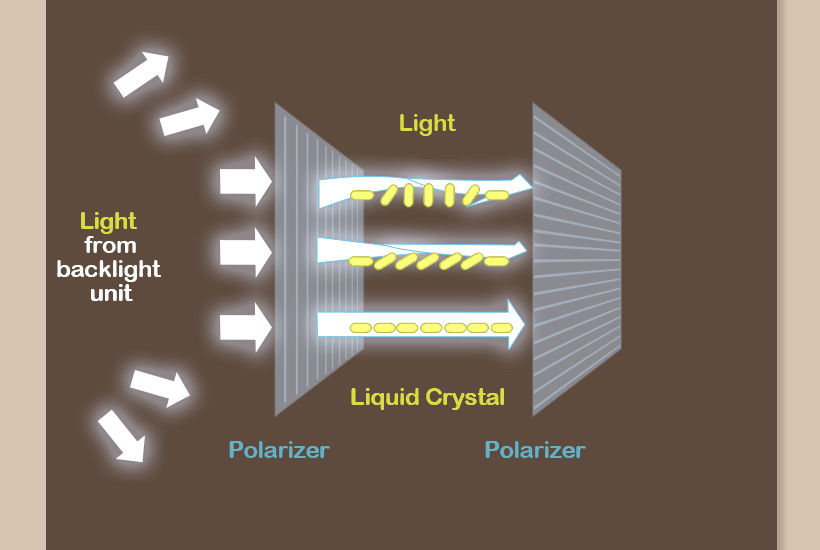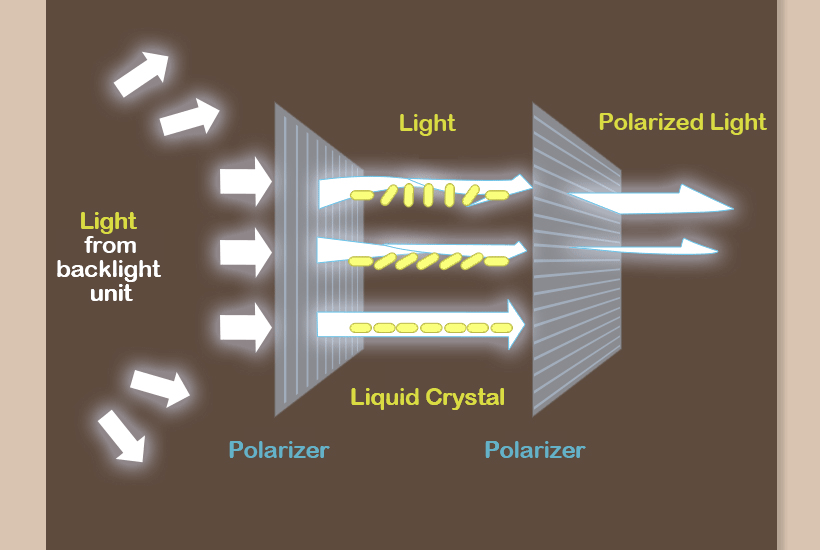
Polarizer is a thin film that allows only a certain orientation of light to pass through. Polarizer is designed to enable light with the same pattern and orientation to transmit and block ones with different orientation.
The LCD adjusts the amount of light by utilizing liquid crystals placed between two polarizers. When light emitted from a backlight passes through the first polarizer, it is polarized to have a certain orientation.
This light then goes through a liquid crystal to have variable angles of lights depending on the liquid crystal’s inclination. When the light passes through the second polarizer, it is either transmitted if it matches orientation of the polarizer or blocked if not. In this way, images are created on the screen.
In the case of OLED that allows pixels light up individually, it doesn’t need the use of backlight unit and two polarizers. Instead, the polarizer, an opaque plastic sheet, is attached to displays to prevent the panel from reflecting external light.
Since a traditional polarizer adds a dark layer of film on top of the panel, your device requires more light – and power – to effectively display, with the transmittance rate reduced by over 50 percent.
Therefore, last August, Samsung Display unveiled its new Eco2 (Eco Square) OLEDTM technology, which first-ever integrates polarizer by leveraging its innovative panel structure.



