Backlight Unit is one of the essential components of the LCDs. There are two types of Display: One is an emissive type that can be self-luminous, and the other is a non-emissive type operated utilizing an external light source. LCDs, unlike OLEDs, do not have an illuminant source, so they require the help of separate light to generate an image on the screen.
In a nutshell, the backlight unit is the part that illuminates light evenly in the entire panel area for the display screen to be turned on. Backlight unit, also known as the acronym ‘BLU,’ is located on the very bottom side of an LCD panel.
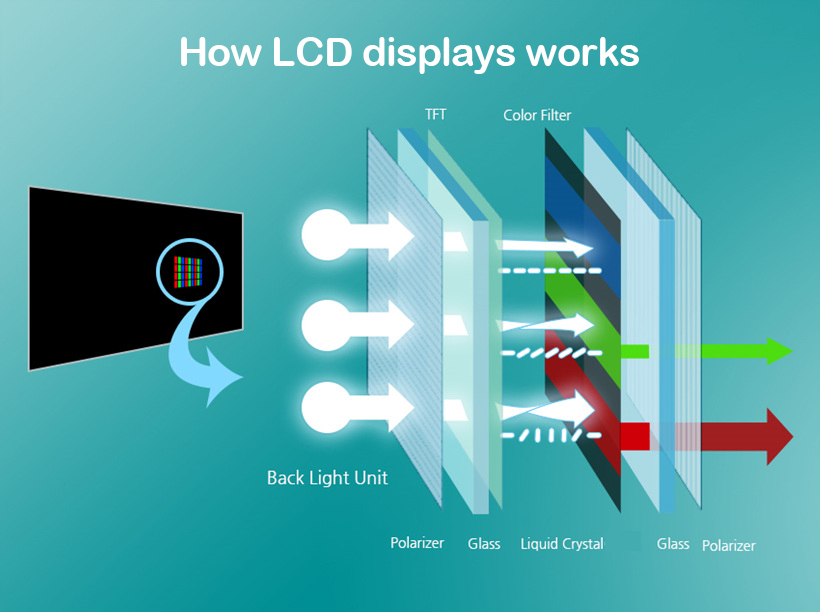
In the LCD structure, when the light comes out from the backlight unit, it passes through a liquid crystal and is tilted to the desired alignment to adjust the amount of light. Which color will be produced is determined after passing through a color filter composed of Red, Green, and Blue. For example, if the tilted liquid crystal completely blocks the passage of light, the display will show black color. However, if the light passes through all RGB sub-pixels, the display will represent white color.
A backlight unit consists of several plastic sheets, as demonstrated below the image.
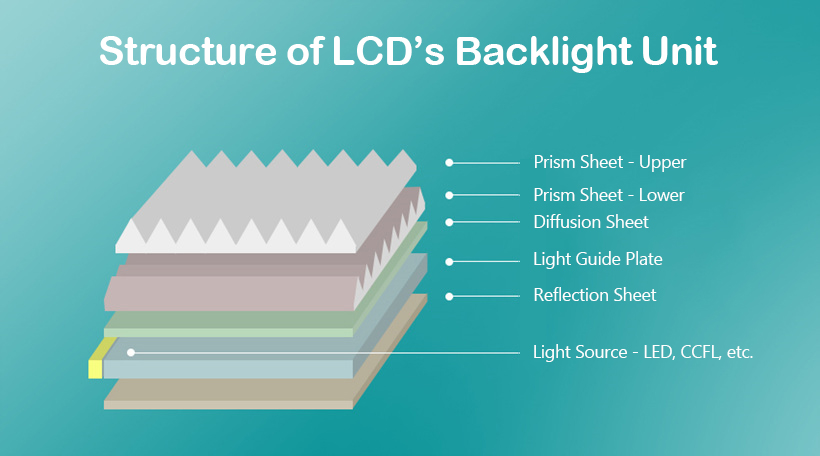
Backlight unit comprises five different sheets - a lamp for a light source, a reflection sheet to reduce light loss, a light guide plate that uniformly spreads out the light over the entire screen area, and a prism sheet to enhance light efficiency.
There are several types of lamps used in the backlight unit. In the early days of LCDs, Cold Cathode Fluorescence Lamp (CCFL) was mainly used for a light source, but recently, it has been replaced with LED (Light Emitting Diode). LED can reproduce a crisp and vivid image with its thinness and high luminance.



