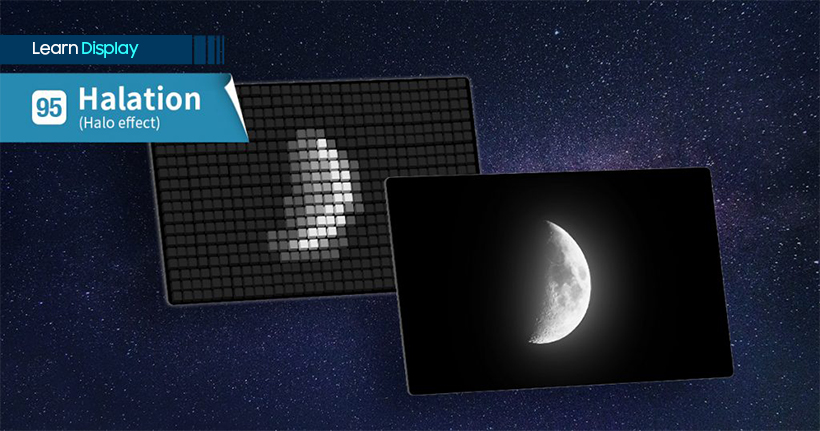
In displays, “halation” refers to a phenomenon where the boundaries in dark areas of a high-contrast image become blurred, like that of a crescent moon in the sky. It is also called the “halo effect.”
Halation often appears in LCD products equipped with local dimming technology. Local dimming was developed for an LCD to reproduce clearer black, by sectioning the LED backlight underneath the panel to either turn off or dim down in dark areas, while increasing the brightness for brighter areas. This reduces the amount of light escaping out of the backlight in an LCD.
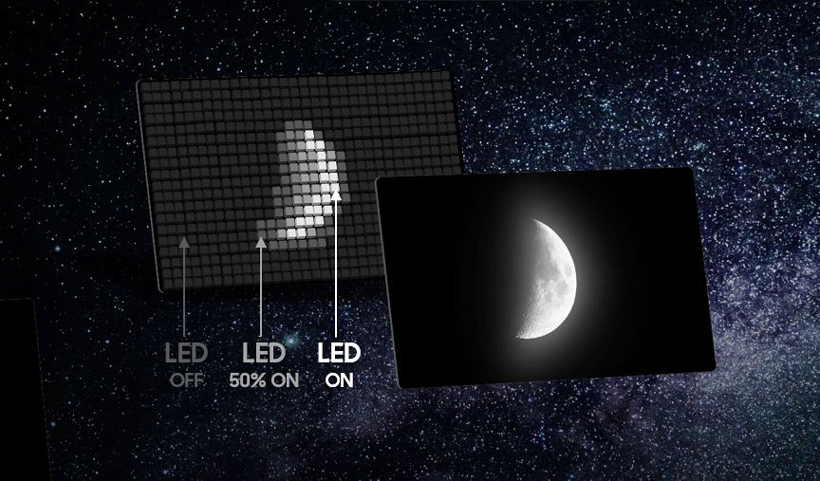
However, local dimming available today is not capable of detailed adjustment of light, but only offers light adjustment by sections. This leads to light escaping out of the backlight, which is turned on for images that are brighter when the display needs to show an image that requires both dark and light colors at the same time. This is the reason why halation occurs, creating a blur in the boundary between the bright and dark areas of an image.

Unlike an LCD, equipped with local dimming, an OLED display does not suffer from halation as it is self-emissive and does not require a backlight, adjusting the brightness in each pixel. This allows for clearer image quality without the halo effect. In 2022, Samsung Display’s laptop OLED display was certified as being halo-free by the global certification organization UL.




