
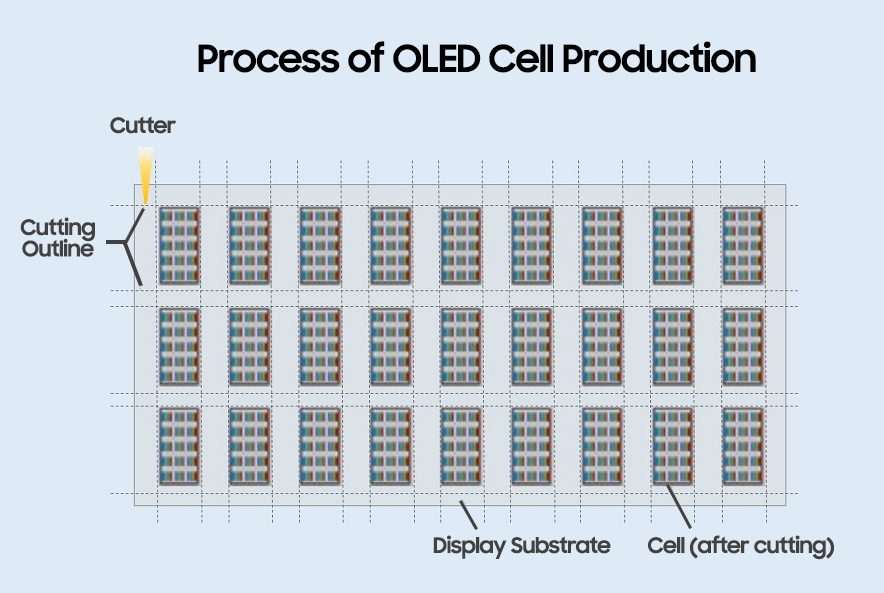
Once a large mother glass undergoes a series of processes in the Fab - such as the thin film transistor (TFT), evaporation, and encapsulation - unnecessary parts are removed and cut into pieces suitable for commercial use in the market: That is what we refer to as an OLED cell.
In other words, to manufacture displays more efficiently, a large sized mother glass is used in the fab before it’s ready to be cut into “cells” for laptop or tablet PC displays as well as smartphone or smartwatches.
The key part of producing these cells is cutting the display substrate, which requires a sharp wheel or laser cutter. Depending on the type of product, cutting methods vary: Generally, a diamond wheel cutter is used to cut hard mother glass used for rigid OLED displays while a laser cutter is used for flexible OLED displays thanks to its excellent processability.
For flexible OLEDs, thin film transistor(TFT) is deposited by placing PI substrate on the glass. Therefore, besides cutting panels, production of cells also includes the glass substrate detachment from the PI substrate.
Once every individual cell has been processed in sizes and shapes tailored to the final products, the next display manufacturing process awaits: Module manufacturing.



