
A bezel refers to the border frame of a computer monitor, smartphone, or any other computing device, excluding the active area where the screens are turned on.
A bezel is often referred to as the dead space of a display, indicating the top, bottom, left, and right sides as well as the corners of a display outside the active area emitting light. The left and right sides of a bezel are reserved for the wiring and circuit for transmitting signals to ensure light emission on pixels.
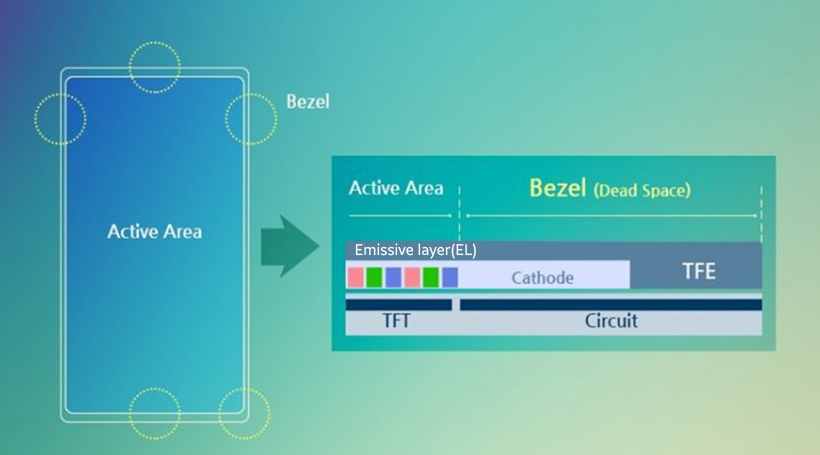
Rather than increasing product size, companies focus on minimizing the bezel to maximize the active area as much as possible as the trend of full-screen smartphones or tablet devices continues. In order to reduce the bezel size, minimizing the wire width or thickness of wires is crucial since bezels contain electrodes and electrical circuits.
‘Narrow bezel’, ‘bezel-less’, and ‘zero bezel’ are some of the many terms created, indicating the amount of attention and effort placed towards minimizing bezels within the display industry.
A method of bonding DDI(Display driver IC) on the panel has also evolved in order to achieve narrower bezels.
The previously used Chip on Film (COF) technique bonds the display driver IC to the flexible printed circuit board (FPCB) so that the FPCB can be bent and hidden behind the display panel. Today, the Chip on Panel (COP) method mounts the driver IC directly onto the panel that can be bent so that the driver IC goes behind the substrate, ultimately minimizing the bezel.
Expanding the active area of a display by reducing dead space not only enhances the immersive experience but also increases the aesthetic appeal of the product.



