
The black matrix (BM) is the black demarcation between the red, green, and blue (RGB) sub-pixels. The black matrix essentially serves as the partition that separates the space for each sub-pixel before the color filter layer for RGB sub-pixels is generated. The black matrix also prevents LCD backlight from bleeding, colors from the RGB sub-pixels from mixing, and leakage current of thin-film transistor (TFT) from increasing due to an external light source.
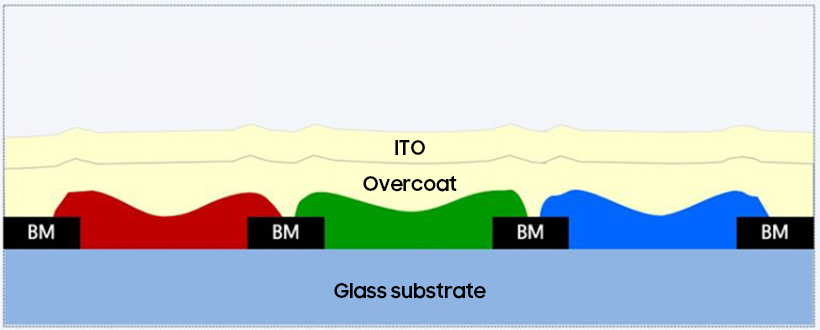
Before the RGB color filters are created on the glass substrate of LCD, the black matrix is patterned by photolithography on the glass substrate. Between each array of black matrix, RGB color filters are deposited; afterward, an overcoat is applied to even out the color filter. Last but not least, a transparent conductive electrode (indium tin oxide, ITO) is deposited on the top of the overcoat layer so that it enables to control the liquid crystals after being bonded to the TFT substrate.
The black matrix refers to the black area between pixels, but it is sometimes interchangeably used to describe the outer frame of a smartphone display, also known as a bezel.



