In the display industry, Excimer Laser Annealing (ELA) refers to a laser process used to create a low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) circuit layer. By converting the amorphous silicon (a-Si) TFT into low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) TFT, the ELA process improves the performance of the thin-film transistor (TFT) significantly.
※ Thin-film transistor (TFT): A silicon-based electronic circuit that controls each pixel to emit the RGB light in a display
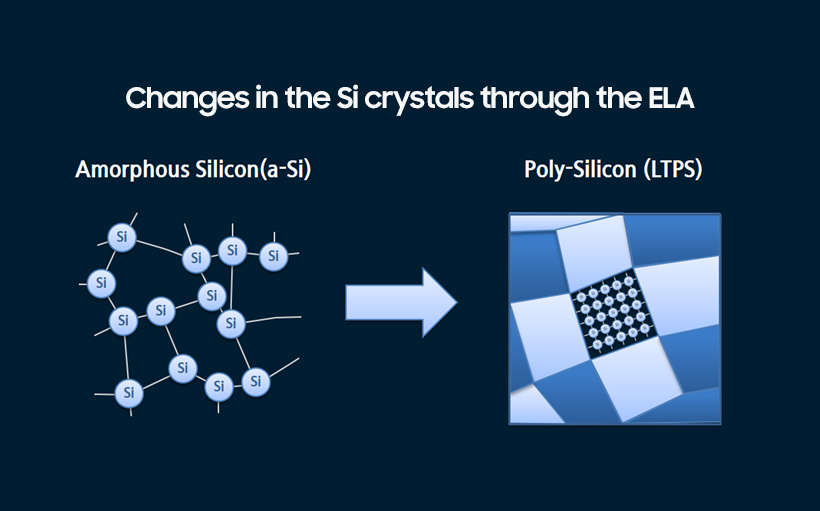
Compared to the traditional a-Si TFT, the LTPS has a more structured composition of silicon crystals, which facilitates better mobility of electrons in the circuit. While a-Si can be compared to an unpaved, narrow road with lots of twists and turns, the LTPS is comparable to a highway with multiple lanes. When fabricating a display with a high resolution, slim bezel, and low power consumption, LTPS has a clear advantage as greater mobility of electrons equals a better flow of power and data.
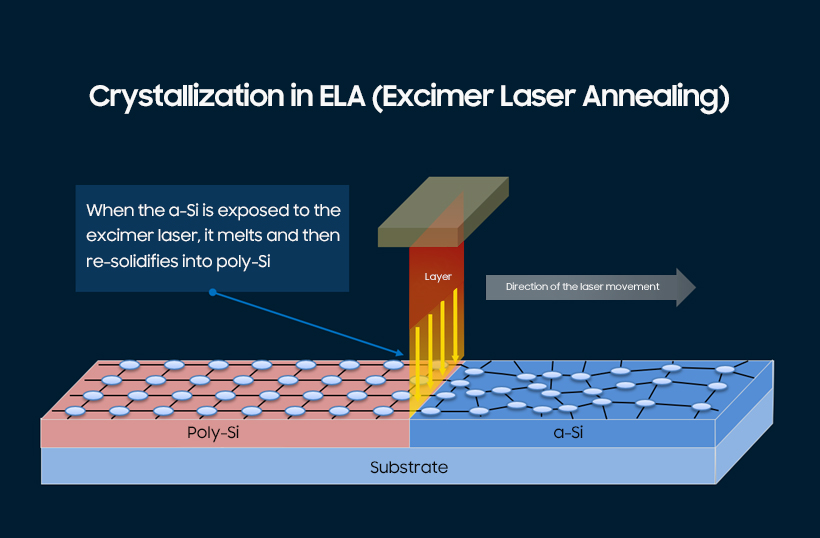
The LTPS is created by processing a-Si under the excimer laser. As seen in the illustration above, when the laser is projected onto the a-Si layer and moves, it results in developing an organized, checkerboard-like particle composition: This process is Excimer Laser Annealing (ELA). Laser-induced modification of a-Si converts into a crystallized poly-Si (LTPS), which significantly improves the performance of the TFT by forming a structured monocrystalline silicon cluster.



